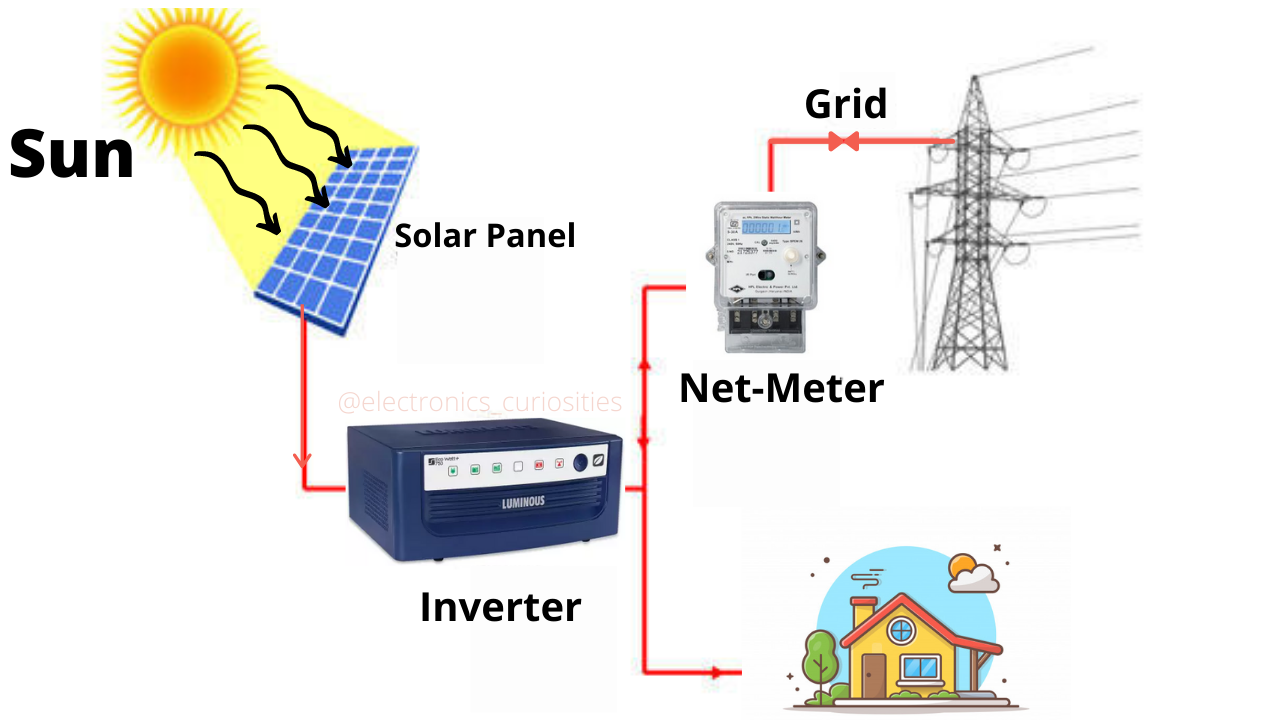
On Grid Solar System
An on-grid solar system, also known as grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is a solar power system that is connected to the electrical grid. Here's how it works:
Solar Panels:
Solar Panels typically mounted on the roof or in an open area with good sun exposure, collect sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic cells.
Inverter:
The electricity generated by the solar panels is in direct current (DC) form. An inverter converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
Grid Connection:
The AC electricity produced by the solar panels is then fed into the main electrical panel of the building, where it can be used to power appliances, lights, and other electrical devices.
Net Metering:
Net metering is used for grid-tied solar systems. With net metering, any excess electricity generated by the solar system that is not immediately used by the building is fed back into the grid. The utility company then credits the owner of the solar system for the electricity produced, effectively spinning their meter backward.
Grid Backup:
During periods when the solar panels are not generating enough electricity to meet the building's needs (such as at night or during cloudy weather), electricity is supplied from the grid as usual. This ensures a constant and reliable power supply.