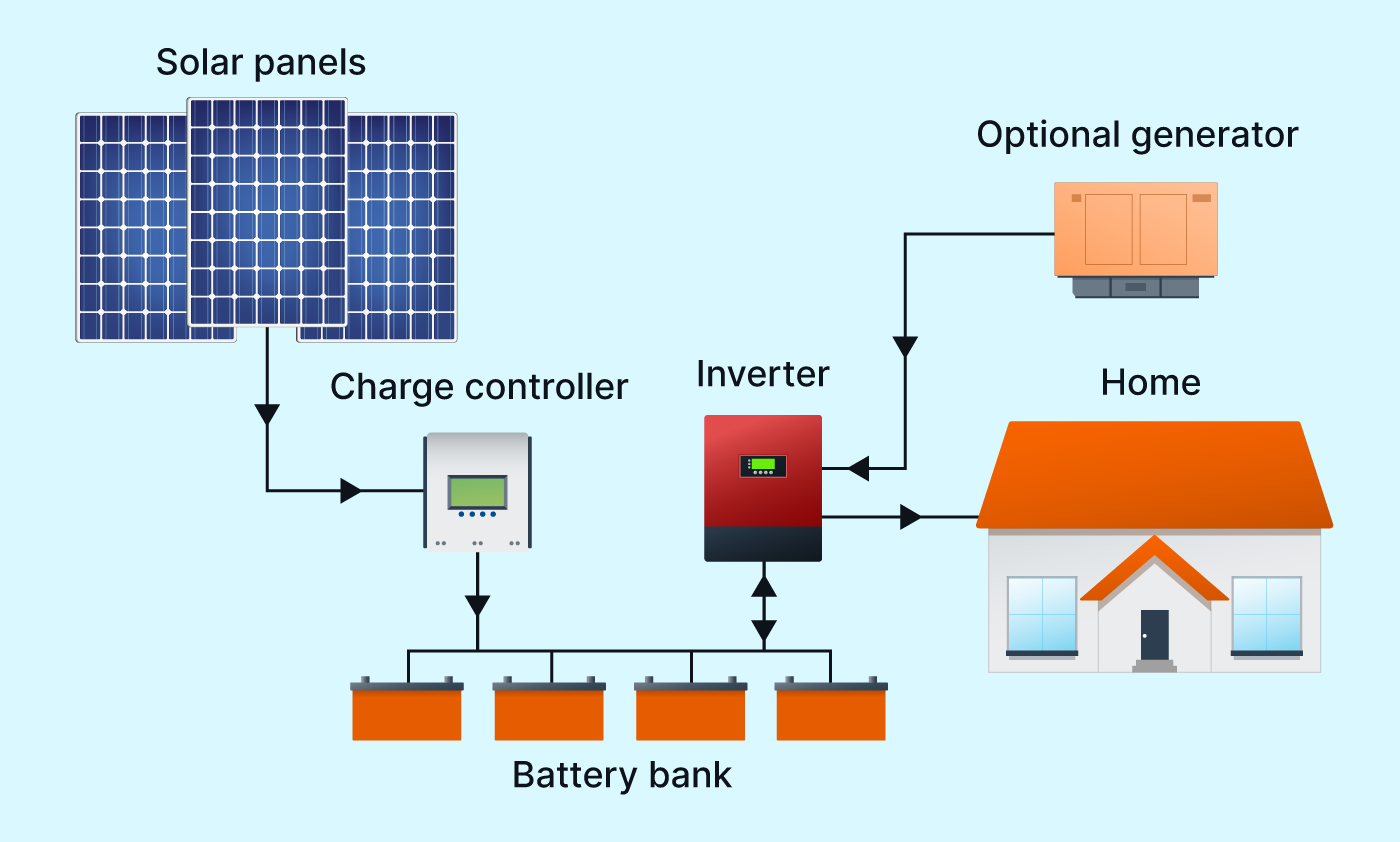
Off-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar system, also known as a stand-alone solar system, operates independently of the electrical grid. It's typically used in remote locations where connecting to the grid is either impractical or too costly. Here's how it works:
Solar Panels:
Off-grid solar systems use solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic cells, just like grid-tied systems.
Charge Controller:
The electricity generated by the solar panels is in direct current (DC) form. A charge controller regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels to ensure that the batteries are charged safely and efficiently.
Battery Bank:
Unlike grid-tied systems, which feed excess electricity into the grid, off-grid systems store excess electricity in batteries for later use. The battery bank stores the electricity generated by the solar panels so that it can be used when there is little or no sunlight available, such as during nighttime or cloudy days.
Inverter:
When electricity is needed, such as to power appliances or lights, it is drawn from the battery bank and converted from DC to alternating current (AC) by an inverter. This AC electricity can then be used to power electrical devices.
Backup Generator (Optional):
In some cases, especially in areas with limited sunlight, an off-grid solar system may include a backup generator fueled by diesel, propane, or another fuel source. This generator can be used to provide electricity when the solar panels are unable to meet demand and the battery bank is depleted.